Magnetic Resonance Elastography
Characteristics
- Spatial Resolution
- ~1 mm
- Temporal Resolution
- ~10 ms
- Maturity
- Established
- Invasiveness
- Non-invasive
Applies external mechanical vibrations with no tissue penetration
- Summary
- Magnetic Resonance Elastography
- Tags
- MagneticAcoustic
- Effects Involved
- STIFFNESS-CHANGE
Details
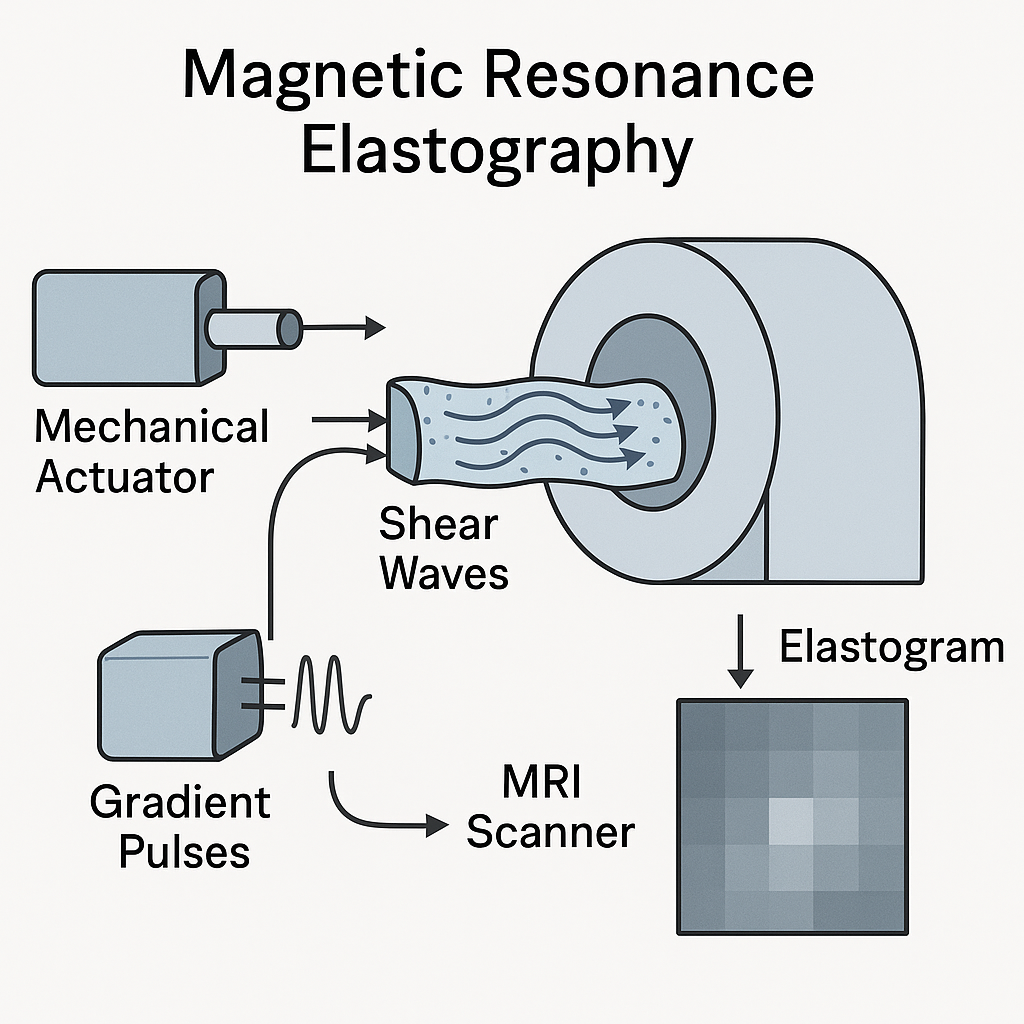 Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) is a non-invasive imaging technique that combines magnetic resonance imaging with externally induced shear waves to quantitatively map tissue mechanical properties. A mechanical actuator vibrates at low frequencies (typically –, –), generating shear waves with wavelengths on the order of – (–), given typical shear wave speeds –. Wave amplitudes in soft tissue are on the order of – (–). These dynamic displacements are encoded into the phase of the MRI signal using oscillating motion-encoding gradients (–), producing a phase shift
Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) is a non-invasive imaging technique that combines magnetic resonance imaging with externally induced shear waves to quantitatively map tissue mechanical properties. A mechanical actuator vibrates at low frequencies (typically –, –), generating shear waves with wavelengths on the order of – (–), given typical shear wave speeds –. Wave amplitudes in soft tissue are on the order of – (–). These dynamic displacements are encoded into the phase of the MRI signal using oscillating motion-encoding gradients (–), producing a phase shift
where is the proton gyromagnetic ratio and the local displacement.
Under harmonic excitation at angular frequency , the displacement field satisfies the Helmholtz equation:
with wave number and shear wave speed . From measured wavelengths () and tissue density , one can estimate the shear modulus in the kPa range (–). For example, yields .
After acquisition of phase images at multiple vibration phase offsets, inverse mechanical modeling or direct inversion algorithms reconstruct spatial maps of shear modulus—elastograms—with voxel sizes of – and stiffness sensitivity on the order of . MRE is sensitive to stiffness-change associated with pathologies such as liver fibrosis ( increases from in healthy tissue to in fibrotic tissue) and brain tumors or neurodegenerative disorders.
Diagram
Literature Review
| Title | Spatial Res. | Temporal Res. | Subjects | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Magnetic resonance elastography with guided pressure waves (2022) Demonstrates a novel MRE approach that guides pressure waves via the buccal cavity to the brainstem and cortex, enabling quantitative mapping of shear viscoelastic moduli in phantoms and in vivo human brains with robust, reproducible displacement fields. | Not specified | Not specified | Phantoms, Humans | Demonstrates a novel MRE approach that guides pressure waves via the buccal cavity to the brainstem and cortex, enabling quantitative mapping of shear viscoelastic moduli in phantoms and in vivo human brains with robust, reproducible displacement fields. |